Ceiling fans are often a popular choice for keeping homes comfortable during warm weather. They work by creating a wind chill effect, which helps people feel cooler without actually lowering the room temperature. This makes ceiling fans an efficient and cost-effective way to enhance comfort without relying solely on air conditioning.
While ceiling fans don’t reduce the temperature in a room, they do improve air circulation, making it feel more refreshing. It’s important to understand how to position and operate ceiling fans to get the best results. For instance, setting the fan direction to counterclockwise during summer can maximize the cooling effect.
Incorporating ceiling fans with other cooling methods can also be beneficial. Using ceiling fans alongside air conditioners or window fans can create a combined effect that optimizes comfort and energy efficiency. By understanding the right techniques and best practices, individuals can effectively use ceiling fans to improve their indoor environment.
Fundamentals of Ceiling Fan Cooling
Ceiling fans improve room comfort by enhancing air circulation and creating a breeze. They achieve this through specific mechanisms that manipulate air movement and impact how people perceive temperature.
Physics of Air Movement
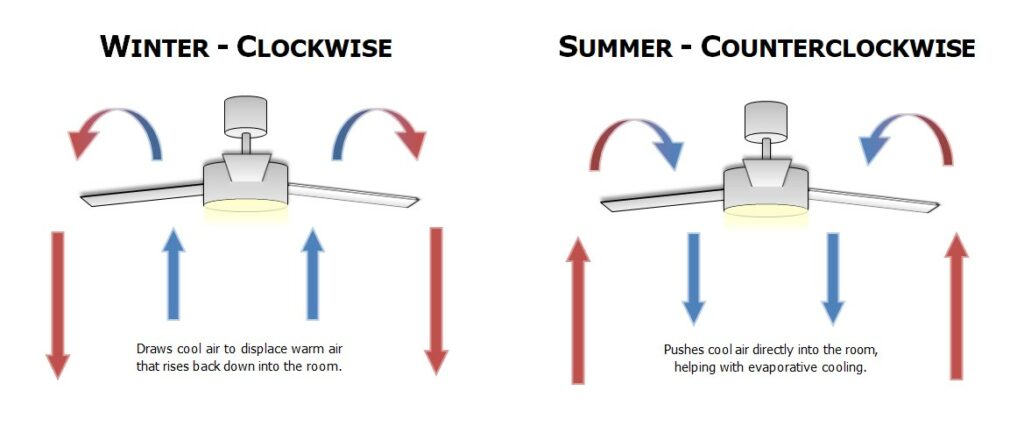
Ceiling fans rotate to move air in the room. When the blades spin counterclockwise in the summer, they push air downward. This breeze makes people feel cooler, even if the actual room temperature doesn’t change.
This cooling effect occurs because the breeze increases the evaporation of sweat from the skin. Faster sweat evaporation leads to a cooling sensation. Additionally, good air circulation prevents stagnant air pockets, ensuring consistent airflow throughout the space.
Role of Ceiling Fans in Thermal Comfort
Ceiling fans contribute to thermal comfort by enhancing perceived coolness without drastically reducing room temperature. When used with an air conditioner, they can allow higher thermostat settings by making the room feel cooler, thus saving energy.
The direction of the fan spin matters. In the summer, a counterclockwise direction creates a pleasant breeze, while in the winter, a clockwise direction pulls cool air up, pushing warm air down from the ceiling. This adjustment helps distribute warmth evenly in the room.
Ceiling fans are effective for personal comfort but do not lower the room’s actual temperature. They are best used as a complementary cooling method along with proper ventilation and air conditioning systems.
Design Considerations
When choosing a ceiling fan, certain design factors play a crucial role in its cooling efficiency. These include the size and pitch of the fan blades, the direction and speed settings, as well as the dimensions of the room and the height of the ceiling.
Fan Blade Size and Pitch
The size of the fan blades impacts how much air the fan can move. Larger blades can push more air, which can enhance the cooling effect. However, blade size must also match the room size to avoid overpowering or underperforming.
Pitch, or the angle of the blades, determines the amount of air a fan circulates. A higher blade pitch means more air movement. Normally, a blade pitch between 12 and 15 degrees offers efficient cooling. A balance between blade size and pitch is vital for optimal performance.
Ceiling Fan Direction and Speed
The direction in which the ceiling fan rotates is essential for cooling. During warmer months, the fan should rotate counterclockwise. This forces the air downward and creates a breeze that helps evaporate sweat from the skin.
Fan speed settings also influence cooling. Higher speeds generate a more pronounced wind chill effect. Users should adjust the fan speed based on the room’s temperature and personal comfort preferences. Controllers and remotes can help make adjustments more convenient.
Room Size and Ceiling Height Impact
The dimensions of the room and the height of the ceiling directly affect the efficiency of a ceiling fan. For larger rooms, a fan with a greater blade span is necessary to ensure adequate air circulation. Standard recommendations suggest:
- Small rooms (up to 75 sq ft): 29-36 inch blades
- Medium rooms (76-144 sq ft): 36-42 inch blades
- Large rooms (145-225 sq ft): 44-50 inch blades
- Extra-large rooms (225+ sq ft): 50-54 inch blades
Ceiling height is also significant. For ceilings above eight feet, a longer downrod may be needed to place the fan at the optimal height, which is typically 8-9 feet from the floor. This ensures both safety and effective air circulation.
Energy Efficiency
Using ceiling fans can significantly reduce energy costs and improve comfort, especially when used in combination with air conditioning. Proper use of ceiling fans optimizes cooling efficiency and energy consumption.
Comparative Energy Usage
Ceiling fans are an energy-efficient way to cool a room. They consume far less electricity compared to air conditioning units. For instance, while an air conditioner can use up to 3,500 watts, a ceiling fan generally uses between 15 to 90 watts, even at its highest setting.
Power Consumption:
- Ceiling Fan: 15-90 watts
- Air Conditioner: Up to 3,500 watts
This difference in power usage means that ceiling fans can circulate air effectively with minimal energy expenditure. Moreover, running ceiling fans only when a room is occupied further enhances energy savings by ensuring that no unnecessary power is consumed.
Effect on Air Conditioning Efficiency
Ceiling fans can work in tandem with air conditioning systems to enhance overall efficiency. By using a ceiling fan, homeowners can set their air conditioner thermostats 4°F higher without sacrificing comfort. The fans create a wind-chill effect, making occupants feel cooler than the actual air temperature.
When air conditioners do not have to work as hard to cool a room, this reduces the total energy used. For optimal performance, ceiling fans should be installed with blades 7-9 feet from the floor and 10-12 inches below the ceiling, ensuring ideal air circulation.
In multi-story homes, where warm air rises, ceiling fans can help distribute cool air more evenly. This consistent airflow can prevent air conditioners from cycling on and off too frequently, leading to more stable indoor temperatures and reduced energy costs.
Operational Guidelines
Ceiling fans can be beneficial year-round if used correctly. Attention to fan direction, regular maintenance, and smart integration with other cooling systems can maximize their efficiency.
Optimal Use During Different Seasons
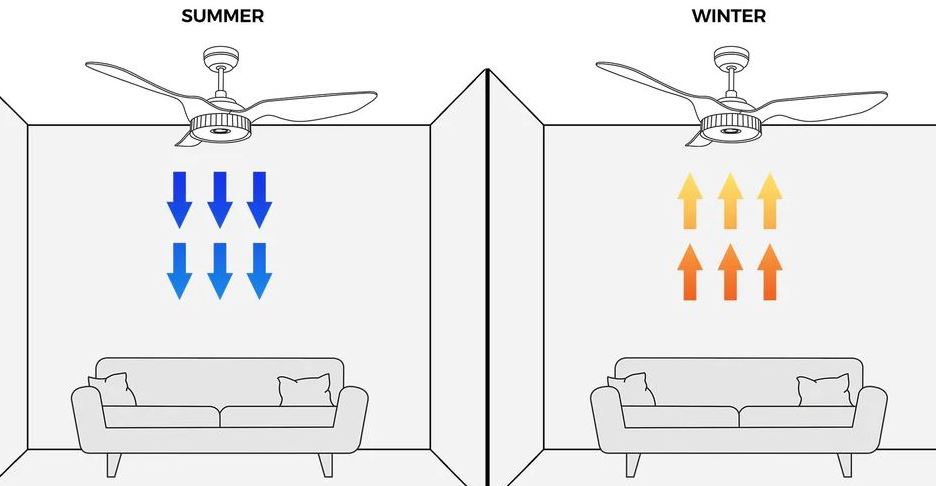
Summer: During the summer months, ceiling fans should rotate counterclockwise. This direction pushes air downward, creating a cool breeze. The airflow helps evaporate sweat, making individuals feel cooler without altering the room temperature.
Winter: In winter, switch the fan direction to clockwise. Set to a low speed, this direction pulls cool air up, pushing warm air down and circulating heat throughout the room. This can reduce heating costs by maintaining an evenly distributed warm air layer.
Maintenance and Care
Routine maintenance ensures that ceiling fans operate efficiently. Dust and dirt can hinder performance, so clean the blades at least once a month.
Check for wobbling: A wobbling fan can cause wear and noise. Balance the blades and tighten any loose screws.
Lubricate moving parts: Some models require oiling to keep the motor running smoothly.
Inspect electrical connections: Ensure that all wiring is secure to avoid potential hazards.
Integration with Cooling Systems
Pairing ceiling fans with air conditioners can enhance cooling efficiency. Set the thermostat a few degrees higher and let the fan circulate the cool air, reducing energy consumption.
Use in conjunction with window fans: Strategically place window fans to draw in cool air and push out hot air.
Combine with portable fans: For large rooms, use both ceiling and portable fans to ensure uniform air distribution.
Proper integration can make any cooling system more effective, providing comfort while saving on energy costs. Ceiling fans, when used thoughtfully, serve as a valuable asset to maintaining a pleasant indoor environment.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of ceiling fans involves their lifecycle and the use of sustainable materials and practices.
Lifecycle of a Ceiling Fan
The lifecycle of a ceiling fan includes manufacturing, transportation, usage, and disposal. During manufacturing, materials such as metals, plastics, and electronic components are used. These materials require energy for extraction and production, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
Transportation also adds to the environmental cost. Fans are often shipped long distances, consuming fuel and emitting carbon dioxide.
In usage, ceiling fans consume less energy than many cooling alternatives, making them an energy-efficient choice. They use around 30-50 watts on average, compared to the much higher consumption of air conditioners.
Finally, disposal poses environmental challenges. Worn-out fans may end up in landfills, contributing to electronic waste. Recycling programs can help minimize this impact by salvaging reusable parts and materials.
Sustainable Materials and Practices
Incorporating sustainable materials in ceiling fan construction can lessen the environmental footprint. Manufacturers are increasingly using recycled metals and plastics, reducing the demand for new raw materials. This lowers the energy used in production and cuts down emissions.
Energy-efficient motors and components further reduce the fan’s energy consumption, making them greener over their operational life.
Practices such as eco-friendly packaging and reducing waste during production also contribute positively. Companies adopting sustainable practices may also engage in carbon offset programs to balance out their emissions.
Choosing ceiling fans designed with sustainability in mind can make a significant difference. These fans often come with certifications indicating their eco-friendly attributes. By opting for these, consumers support a market shift toward greener products.
Installation and Safety
Proper installation and careful attention to safety standards are crucial when installing ceiling fans. This ensures optimal performance and longevity while minimizing risks.
Correct Installation Procedures
When installing a ceiling fan, first ensure that the electrical box can support the fan’s weight. Fan-rated electrical boxes are essential for this purpose. Begin by turning off the electricity at the circuit breaker to avoid any hazards.
Next, carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions. This usually involves attaching the mounting bracket to the electrical box and securely connecting the fan’s wiring to the house wiring – ensure you are using the correct gauge wires as well. Use wire nuts and electrical tape for secure connections.
After wiring, mount the fan to the bracket. Lastly, attach the fan blades and canopy. Make sure all screws and fasteners are tight to prevent wobbling.
Safety Precautions and Standards
Safety is paramount when installing a ceiling fan. Always ensure the fan is mounted on a fan-rated electrical box, as standard boxes may not support the weight. Use a circuit tester to confirm the power is off before starting any work.
Proper ladder use is crucial. Use a sturdy ladder and follow ladder safety guidelines to prevent falls. Ensure your workspace is well-lit.
Fans should be installed with a clearance of at least 7 feet from the floor, and the blades should be at least 8 to 10 inches from the ceiling. Ensure there is a clear path for the fan blades to prevent any obstructions.
Additionally, regularly check and tighten all connections and screws after installation to maintain safety and performance. Following these precautions will help prevent accidents and ensure safe, efficient operation.